Guidelines for natural ventilation by use of ventilated windows
Natural ventilation is a sustainable and energy-efficient solution for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. Ventilated windows play a crucial role in this process, allowing fresh air to enter and stale air to exit a building. To ensure effective natural ventilation, it is essential to follow specific guidelines and rules of thumb.
Read more about natural ventilationWhat is required to benefit from natural ventilation?
In order to benefit from natural ventilation, it is essential to understand the specific requirements associated with different ventilation strategies. Factors such as window openings and the geometry of the space play a crucial role in determining the most effective ventilation strategy for a project.
Window openings, for instance, can be strategically placed to allow for optimal airflow and circulation. Additionally, the overall design and layout of the space can influence the effectiveness of the ventilated windows. By considering these factors and tailoring the ventilation strategy to suit the project's unique requirements, one can fully harness the benefits of natural ventilation and increase indoor air quality.
Geometry of space
To benefit from natural ventilation, it is recommended to have a room height of at least 2.5 metres or 8.2 feet but preferably 2.7 metres or 8.9 feet or higher. The room depth should not exceed 2.5 times the room height and should never exceed 10 metres or 33 feet for single-sided ventilation. For cross ventilation, the room depth should not exceed 5 times the room height. Additionally, for stack ventilation, the distance from the facade to the roof lights should not exceed 5 times the room height.
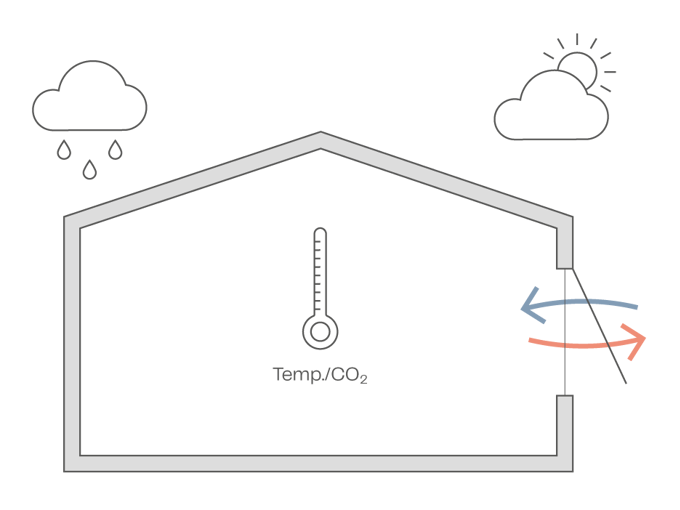
Window openings
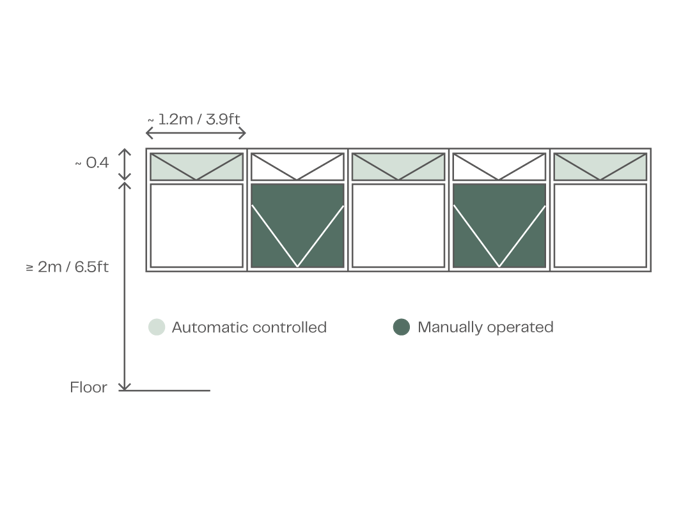
When it comes to window openings in a building's facade, there are certain requirements that need to be met. Firstly, it is preferable for the windows to be positioned at a height of 2 metres or 6.5 feet above the floor level and with sufficient clearance between the top of the vent and ceiling for inward opening vents so as not to limit the achievable opening area. In terms of the type of windows, bottom-hung inward windows or top-hung outward openings are recommended. These options provide flexibility in terms of ventilation and can be adjusted according to individual preferences. The height of the windows in the facade should be approximately 400-600 millimetres or 15.7-23.6 inches. And when it comes to the width of the windows, it is often optimal for them to be around 1.2-1.4 metres or 3.9-4.6 feet because if the width exceeds this range, it may require the use of two window actuators. However, this is subject to the material and type of window profile, as the frame may flex if there is only a single pull point. It is also important to evenly distribute the window openings throughout the facade. This ensures a balanced and aesthetically pleasing design while also allowing for proper airflow and ventilation.
Find your window actuator
Other natural ventilation guidelines
- Optimised natural night cooling
- Preferably include thermal mass for optimum benefit of night cooling.
- User control, for example, timed override facility by local keypads.
- Preference for cross ventilation, stack ventilation or hybrid ventilation in high occupancy spaces, for example, in classrooms.
- Preferably a minimum of 7m3 per person in classrooms.
- Maximum air changes:
- Winter: Approximately 2.5 - 3 h-1 (average during occupied hours).
- Summer: Workstations: 4 - 6 h-1 can easily be accepted.
- Atriums and similar transient spaces where people stay for shorter periods: 10 – 15 h-1 can be accepted.
Specifically for supplementary mechanical exhaust
- In most cases the capacity of the exhaust should be at least the minimum required air change.
- The exhaust should be controllable by variable speed.




